Ultimate Guide to Incident Response Scenarios
Prepare your organization for cybersecurity incidents with effective response strategies, training, and the right tools.

Cybersecurity incidents can disrupt operations, harm finances, and damage trust. Being prepared is essential. This guide simplifies incident response planning and training, helping teams respond effectively to threats like ransomware, data breaches, and insider attacks.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
- Key frameworks (SANS, NIST): Step-by-step strategies for handling incidents.
- Incident response essentials: Defined roles, communication protocols, and recovery steps.
- Scenario training: Simulate real threats to improve team coordination and decision-making.
- Common threats: Practical steps for malware, data breaches, insider threats, and DDoS attacks.
- Tools: Automation and simulation software to streamline response efforts.
Takeaway: Build a clear plan, train regularly, and use the right tools to stay ahead of cybersecurity threats.
Basic Principles of Incident Response
Handling security incidents effectively requires having clear frameworks and detailed plans in place before any threats arise.
Standard Incident Response Frameworks
Two commonly used models for incident response are the SANS and NIST frameworks. Both offer structured methods for managing security incidents, though their approaches differ slightly.
The SANS framework includes six phases:
- Preparation: Build and train your response team.
- Identification: Detect and confirm incidents.
- Containment: Minimize the impact by isolating affected systems.
- Eradication: Eliminate the threat from your environment.
- Recovery: Restore systems to normal operation.
- Lessons Learned: Review the incident and improve processes.
The NIST framework outlines four key phases:
| Phase | Key Activities | Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Form teams, deploy tools, create policies | Build response capabilities |
| Detection & Analysis | Monitor alerts, verify incidents, assess impact | Quickly identify threats |
| Containment & Eradication | Isolate threats, clean systems, patch vulnerabilities | Stop the spread of incidents |
| Post-Incident Activity | Review documentation, improve processes, train teams | Enhance future responses |
These frameworks provide the foundation for creating a thorough response strategy.
Parts of an Incident Response Plan
To make these frameworks actionable, organizations need a well-documented incident response plan. A good plan includes defined roles, communication protocols, documentation standards, and recovery procedures.
1. Team Structure and Roles
Assigning specific roles ensures a coordinated response:
- Incident Commander: Oversees the entire response process.
- Technical Lead: Manages the technical investigation and resolution.
- Communications Officer: Handles both internal and external updates.
- Documentation Specialist: Keeps detailed records of all actions and findings.
2. Communication Protocols
Effective communication is critical during an incident:
- Establish primary and backup communication methods.
- Define escalation procedures based on incident severity.
- Maintain an updated contact list for all stakeholders.
- Use pre-written templates for updates and notifications.
3. Documentation Requirements
Thorough documentation supports both real-time response and post-incident review:
- Track incident timelines and actions taken.
- Record system changes and configurations.
- Outline evidence collection steps.
- Note key decisions and the reasoning behind them.
4. Recovery Procedures
Detailed recovery steps help restore normal operations efficiently:
- Prioritize which systems to restore first.
- Include data backup and recovery steps.
- Address service level agreement (SLA) requirements.
- Factor in business continuity needs.
Regular testing and updates are essential for keeping the plan effective. Teams should review and revise their plans quarterly, using insights from real incidents and practice drills to make continuous improvements.
Why Teams Need Scenario Training
Scenario training is a critical tool for incident response teams to get ready for security threats. These structured practice sessions help teams fine-tune their coordination and build habits that are crucial for handling real-world incidents.
How Scenario Training Helps
This type of training enhances key skills like quick response, teamwork, situational awareness, and decision-making under pressure.
Boosting Team Performance Through Practice
By simulating real-world challenges without real consequences, scenario training allows teams to:
Build Instinctive Responses
Repetitive practice helps team members internalize procedures, so their actions feel automatic when facing actual incidents.
Manage Stress Effectively
Frequent exposure to simulated crises trains teams to:
- Stay focused during high-pressure situations
- Stick to established protocols despite distractions
- Make evidence-based decisions
- Communicate clearly and efficiently
Enhance Team Collaboration
Practice sessions help clarify individual roles, improve communication, and encourage leadership growth within the team.
These benefits prepare teams to handle a wide range of security challenges with confidence.
Common Response Scenarios
Being ready for various incidents is key. These scenarios help sharpen both technical and communication skills through practical challenges.
Handling Malware and Ransomware
Dealing with malware and ransomware demands quick, coordinated action.
Initial Detection and Containment
- Isolate affected systems immediately to prevent further spread.
- Preserve forensic evidence for later analysis.
- Keep an eye on system indicators to understand the scope of the attack.
System Recovery
- Boot affected systems in safe mode to limit potential damage.
- Use updated tools to scan and clean infected systems.
- Remove malware and restore from clean, verified backups.
Prevention Steps
- Use endpoint protection tools to block threats.
- Regularly check the integrity of backups.
- Apply network segmentation to limit access.
- Continuously monitor system behavior for anomalies.
Managing Data Breaches
Technical Response
- Identify and document which data has been compromised and locate security gaps.
- Strengthen security controls to prevent further breaches.
- Keep monitoring for any unauthorized access attempts.
Legal and Communication
- Notify affected individuals in accordance with legal requirements.
- Report the breach to regulatory authorities.
- Maintain thorough documentation of all response steps.
- Prepare clear public statements if disclosure is necessary.
Follow-Up Actions
- Conduct a detailed forensic analysis to understand the breach.
- Update security policies to address identified weaknesses.
- Improve monitoring tools and processes.
- Tighten access controls to limit future risks.
These steps help build a stronger response system for future incidents.
Responding to Internal Threats and DDoS Attacks
Internal Threat Response
- Watch for unusual user behavior that might indicate an insider threat.
- Track any unauthorized access attempts and policy violations.
- Document incidents carefully and preserve evidence for investigation.
DDoS Attack Mitigation
- Enable traffic filtering to block malicious requests.
- Scale infrastructure capacity as needed to handle increased traffic.
- Work with your ISP to implement upstream filtering.
- Continuously monitor system performance during the attack.
Regular practice and updates to response plans are essential as threats evolve and organizational needs change. Teams should aim to act quickly without sacrificing accuracy or effectiveness.
Building and Testing Response Scenarios
Creating Practical Scenarios
Effective incident response scenarios should mimic real-world challenges in a controlled environment. Start by pinpointing the most likely threats and identifying critical assets that need protection within your organization.
Core Scenario Components
- Define clear goals and success criteria
- Introduce realistic technical challenges
- Set strict time limits
- Ensure reliable communication methods
Key Elements for Realism
- Use actual system setups
- Simulate authentic attack methods
- Reflect typical operational hours
- Introduce communication hurdles
- Add decision-making pressure points
For added complexity, combine multiple threats, like ransomware alongside a DDoS attack, to challenge your team's ability to manage multiple issues at once. Use clear performance metrics to evaluate how well these scenarios are handled.
Measuring Scenario Success
Once your scenarios are in place, focus on assessing their effectiveness. Key metrics include how quickly a response is initiated, how well threats are contained, and the total time required for resolution. Also, track communication efficiency and the accuracy of technical actions.
Running Post-Scenario Reviews
After gathering data, conduct a thorough review to refine your future response strategies. Aim to complete this review within 24 hours to ensure insights are fresh and actionable.
Review Structure
- Record all actions taken during the scenario
- Break down key decision points
- Examine communication effectiveness
- Analyze resource use
- Check alignment with established procedures
Implementing Improvements
Turn the findings from your review into concrete updates. Revise response playbooks and adjust training programs to address identified gaps. Create a timeline that captures detection, critical decisions, response actions, and resolution milestones to pinpoint areas needing improvement. These updates will help your team stay prepared for future challenges.
Tools for Better Incident Response
Handling modern incidents effectively requires tools designed for quick detection, management, and resolution.
Response Automation Tools
Automation tools help monitor systems continuously, detect threats, and respond instantly.
Here’s what they offer:
- Real-time alerts to quickly identify and contain threats
- Automated ticketing for creating, assigning, and escalating issues
- Integration options like APIs and webhooks to connect with your security systems
Training Simulation Software
Simulation software creates virtual environments where teams can practice handling incidents in realistic scenarios.
Key features include:
- Virtual labs that mimic production environments
- Tools to track performance and generate analytics
- Customizable scenarios tailored to specific needs
- Collaboration features to enhance team coordination
- Progress tracking and detailed reporting
This software builds hands-on skills that complement formal response plans.
HelpJam's Response Features
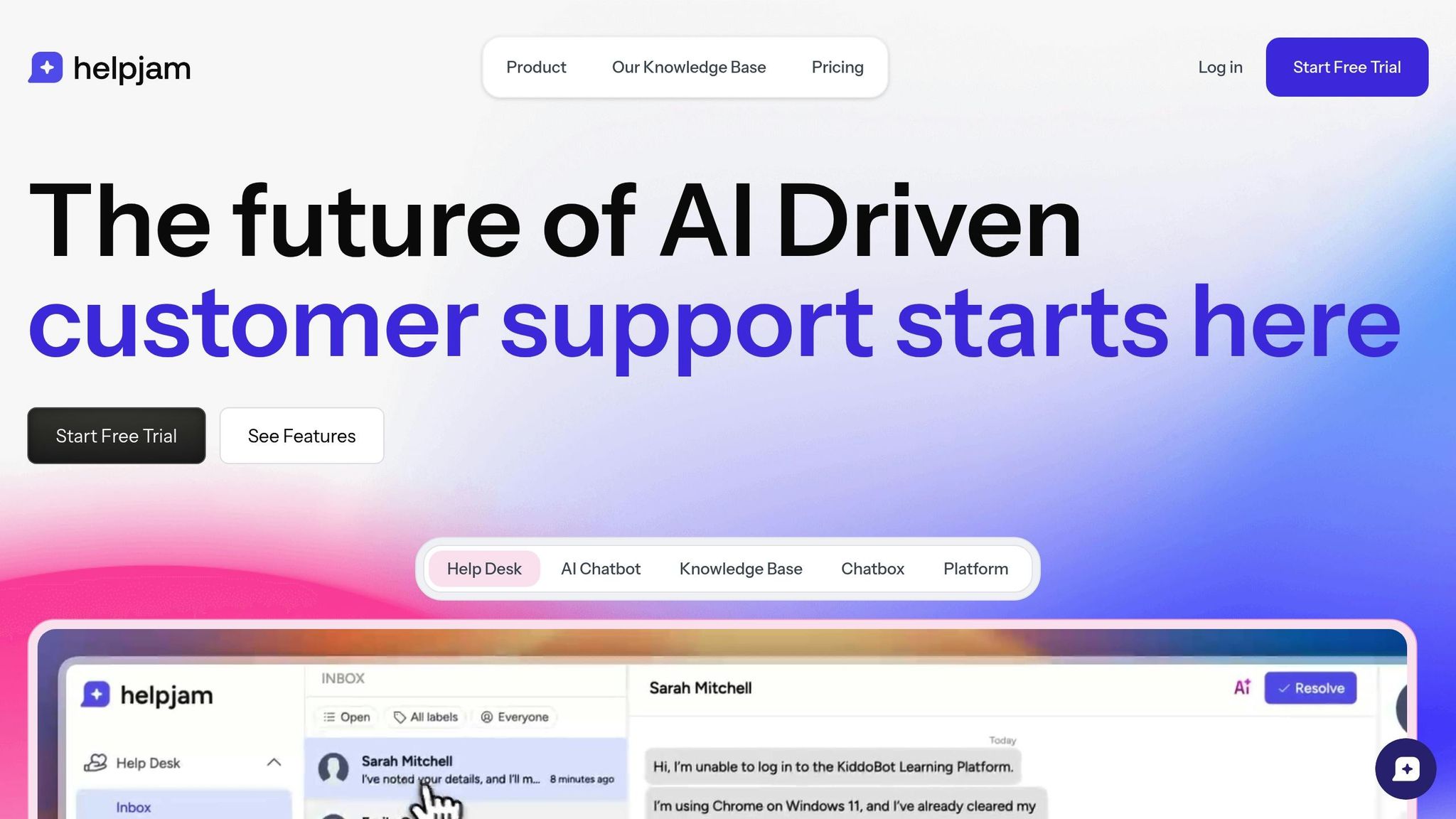
HelpJam combines automation and collaboration tools to simplify incident response workflows. Its main features include:
- Unified inbox: A central hub for incident-related communication, ensuring nothing falls through the cracks
- AI-powered analysis: Automatically summarizes conversations and suggests responses to speed up resolutions
- Real-time tracking: Dashboards that monitor response times and resolution rates, keeping teams ahead of issues
- Smooth escalation: Effortless handoff from AI-driven support to human intervention for complex cases
HelpJam’s AI Chatbot can also be trained using your existing knowledge base. It handles routine queries efficiently while prioritizing urgent issues. Plus, the chatbox can be customized to display support options based on incident type or severity.
| Feature Type | Capability | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| AI | Conversation summary | Faster incident assessment |
| Analytics | Performance tracking | Improved response effectiveness |
| Integration | API/webhook support | Connected workflows |
| Collaboration | Shared inbox | Better team coordination |
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
Effective incident response depends on having well-defined frameworks, practical training, and advanced tools. Organizations that prioritize these elements can improve their overall security measures.
Here’s what matters most:
- Frameworks: Use structured protocols to guide response efforts.
- Regular Training: Practice with real-world scenarios to ensure teams are prepared.
- Advanced Tools: Leverage AI and automation to speed up detection and response.
- Continuous Improvement: Test and refine procedures regularly to address new challenges.
Use these guidelines to enhance your approach.
Next Steps
Here's how to strengthen your incident response plan:
-
Evaluate Your Current Readiness
- Compare your existing response plans to industry standards.
- Look for any gaps in procedures or resources.
- Measure team performance to identify areas for improvement.
-
Integrate AI-Powered Tools
- Use tools that provide instant alerts and actionable insights.
- Consider platforms like HelpJam for smoother workflows.
- Implement systems for real-time tracking of incidents.
-
Plan and Conduct Training
Focus Area Frequency Technical Skills Monthly workshops Communication Quarterly drills Tool Proficiency Bi-weekly sessions -
Monitor and Adjust
- Track how effective your responses are over time.
- Update your plans to address new security threats.
- Keep a record of lessons learned to inform future improvements.
FAQs
What is the difference between the SANS and NIST incident response frameworks, and how can I choose the best one for my organization?
The SANS and NIST incident response frameworks are two widely used models for managing cybersecurity incidents, but they differ in structure and focus. The SANS framework is a straightforward, six-step process designed for simplicity and quick implementation, making it ideal for organizations that need a practical, easy-to-adopt approach. On the other hand, the NIST framework offers a more detailed, comprehensive methodology, emphasizing preparation and continuous improvement, which is better suited for organizations with complex systems or regulatory requirements.
To choose the right framework, consider your organization's size, industry, and specific needs. If you’re looking for a quick, actionable strategy, SANS might be the best fit. If you require a more robust, adaptable process, NIST could be the better option. Both frameworks are effective, so the key is aligning your choice with your operational goals and resources.
How does scenario-based training improve incident response teams, and what are the best practices for running these sessions?
Scenario-based training improves incident response teams by offering practical, hands-on experience in a controlled environment. It allows team members to practice their roles, refine procedures, and identify potential weaknesses without the pressure of a real incident. This approach builds confidence and ensures teams are better prepared to handle real-world challenges effectively.
To get the most out of these sessions, focus on a few key best practices:
- Set clear objectives: Define specific goals for each scenario to ensure the training is purposeful and targeted.
- Design realistic scenarios: Create scenarios that closely mimic real-world incidents, such as system outages or cyberattacks, to make the training as practical as possible.
- Debrief thoroughly: After each session, review what worked, what didn’t, and how the team can improve for future incidents.
Incorporating tools like AI-driven chatbots and knowledge bases into these exercises can also simulate real-time problem-solving, helping teams prepare for customer-facing challenges more effectively.
What tools can help automate and improve incident response, and how does AI enhance organizational preparedness?
To streamline and automate incident response, tools with AI-powered features are essential. These tools can help summarize interactions, generate accurate responses, and extract key insights to improve efficiency. AI also enables realistic simulations and predictive analysis, helping organizations better prepare for potential incidents.
Platforms like HelpJam integrate AI into workflows, allowing teams to provide faster, more accurate support by leveraging trained chatbots and automated processes. This ensures your organization is always ready to respond effectively while maintaining high customer satisfaction.





